If you’re preparing documents for courts, ministries, universities, or embassies in the Kingdom, understanding the certified translation process in Saudi Arabia is essential. This cluster guide breaks down the end-to-end workflow used by recognized providers in KSA so you can move from document intake to final attestation without delays. For a broader foundation on definitions, legal contexts, and acceptance criteria, see our main resource:
Read complete overview: “Certified Translation Saudi Arabia: The Complete Guide to Legally Accepted Documents.”
As a Saudi-based provider, C-KAT Translations and Interpretations delivers compliant, confidential, and officially recognized translations across sectors. Below, we share the practical steps and quality safeguards we follow to ensure your documents are accepted by government entities, courts, and embassies in Saudi Arabia.
Table of Contents
1) The Document Translation Procedure in KSA: What “Certified” Means?
In Saudi Arabia, a “certified translation” is a translation completed by an officially recognized office and issued on letterhead with a statement of accuracy, translator or office seal/signature, and contact details. Many public and private bodies require this formality, including the Ministry of Justice (MOJ), the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA), courts, universities, licensing bodies, and foreign embassies. Requirements can vary by institution, but the following components are common:
- Formal accuracy statement and liability acknowledgment by the translation office
- Translation certification and stamping on official letterhead
- Official document formatting in KSA style conventions (pagination, footers, and reference to source details)
- Attachments: copies of the source documents; sometimes attested originals are requested by the authority
Tip: Always check whether the receiving authority needs originals, notarization, or additional legalization (e.g., MOJ/MOFA). If you’re unsure, our team can verify acceptance criteria on your behalf before translating to avoid rework.
2) At-a-Glance Flow: From Intake to Embassy Acceptance
Here is a high-level map of the document translation procedure KSA-wide.
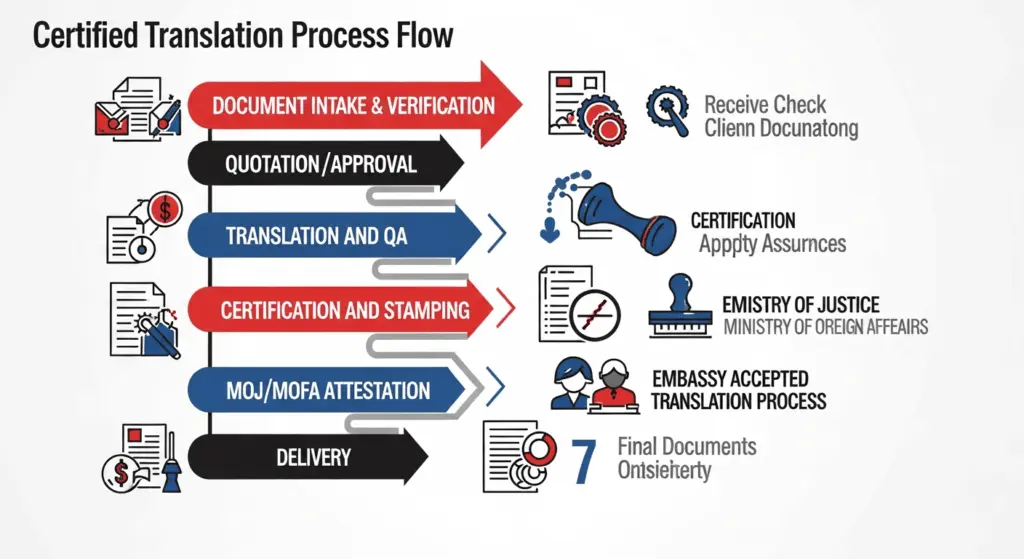
- Document intake and verification: Confirm legibility, completeness, and intended authority (e.g., MOJ, MOFA, or embassy).
- Scope and quote: Word count, language pair, complexity, and urgency assessed.
- Translator assignment: Specialized, native linguists with subject expertise (legal/medical/technical).
- Terminology and transliteration standards: Names, titles, and official terms are standardized.
- Draft translation and quality assurance: Multi-layer review to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Official formatting and certification: letterhead, stamps, signatures, and traceability details.
- Legalization and attestation steps (if required): notarization, MOJ/MOFA, and embassy legalization.
- Delivery: Printed sets and secure digital copies, as the receiving entity permits.
3) Step-by-Step Certified Translation Saudi Arabia: Detailed Checklist
Use this practical checklist to avoid common pitfalls and keep timelines on track.
- Document intake and verification
- Provide clear scans of the entire document (front/back, seals, and QR codes).
- Share your target authority (e.g., MOJ court filing, MOFA attestation, specific embassy) and purpose (immigration, licensing, academic, litigation).
- Confirm whether the authority requires originals, certified copies, or pre-attestation (e.g., by your issuing university or Chamber of Commerce).
- Quotation and timeline confirmation
- Costs depend on language pair, volume, subject complexity, and urgency.
- For a fast certified translation process, ask about prioritized workflows or partial deliveries for staged submissions.
- Agree on output format (hard copy sets, e-signed PDF, or both) and delivery method (pickup, courier in Saudi Arabia, or secure email).
- Translator assignment and confidentiality
- Assign a native-language linguist with relevant domain knowledge (e.g., legal, medical, technical, or academic).
- Ensure NDAs and secure file handling policies are in place for sensitive data.
- Terminology and transliteration standards
- Names and places: Align with passport or national ID for consistent transliteration.
- Official titles and job roles: Use MOJ-accepted and sector-standard equivalents where appropriate.
- Keep a running glossary for recurring terms to maintain consistency across multiple documents.
- Draft translation and quality assurance translation
- Dual review: The translator and an independent reviewer apply linguistic and legal accuracy checks.
- Numeric accuracy: Verify dates (Hijri/Gregorian), figures, and reference numbers.
- Completeness: Ensure seals, stamps, certifications, QR codes, and annexes are represented in-text (e.g., “Stamp: Ministry of… [illegible]”).
- Official document formatting KSA
- The letterhead and footer should identify the translation office, the address in Saudi Arabia, and the contact details.
- Pagination and cross-references to the source document identifiers (serial, file, or reference number).
- Please include an accuracy statement and date of issue; if there are multiple pages, kindly seal or stamp each page as required.
- Translation certification and stamping
- Please affix the office stamp and include the authorized signature. Some authorities prefer wet stamps on firm copies.
- Provide a cover page summarizing document type, language pair, and receiving authority if beneficial.
- Attach a copy of the source documents behind the certified translation for traceability.
- Notarization requirements Saudi Arabia
- Not needed for all cases. Some courts or foreign embassies request notarized affidavits confirming the translator’s credentials and accuracy.
- Corporate documents may require Chamber of Commerce verification before or after translation, depending on the target authority.
- Legalization and attestation steps
- For Saudi entities: MOJ certification may be needed for court-related documents; MOFA attestation may be required for use outside KSA.
- For foreign use: After MOFA, proceed to the relevant embassy/consulate for the final stamp as part of the embassy-accepted translation process.
- Timeframes vary by authority; plan buffer days for appointments or e-platform processing.
- Delivery and archiving
- Please provide the number of original certified sets required by the authority and keep an extra set for your records.
- Request secure digital copies (locked PDFs) where permitted for online submissions.
4) MOJ Translation Requirements, MOFA, and Embassies: What to Expect
While exact requirements can vary by case and authority, here are common patterns to help you prepare:
- MOJ translation requirements: Court filings and legal documents often require certified translations with complete fidelity to source layout and content. Expect wet stamps, signatures on each page, and explicit accuracy statements.
- MOFA attestation: Frequently requested when documents are destined for use abroad. The sequence may require prior attestations (e.g., by MOJ or source country authorities) before MOFA will stamp.
- Embassy acceptance: Many embassies in Saudi Arabia require certified translations issued by recognized offices and may request notarization or additional embassy-specific forms. Always verify current requirements in advance.
Royal Consulate General of Saudi Arabia. (n.d.). Instructions for attestationPDF. Saudi Ministry of Foreign Affairs. https://embassies.mofa.gov.sa/sites/pakistan/EN/karachi/AboutDiplomaticMission/SiteAssets/Pages/Consulate-Services/%E2%80%A2Instructions%20for%20%20Attestation.pdf
Note: The order of attestations matters. In many cases, you’ll legalize the original document first (in its country of origin), then translate it in KSA, and finally obtain MOFA and embassy stamps. For Saudi-issued documents, you may translate first and then proceed with MOJ/MOFA steps as directed. Because rules evolve, consult C-KAT to confirm the correct path for your case.
5) Arabic to English Translation Process KSA: Examples and Naming Conventions
The Arabic-to-English workflow requires special attention to transliteration and official terminology. Here are common examples and how we handle them:
- Personal IDs and names: We match spellings to passports or national IDs. If multiple spellings exist (e.g., Mohammad/Muhammad), we standardize to your official document.
- Dates: Convert Hijri to Gregorian with the correct format, and footnote or parenthetically include the original if required by the receiving authority.
- Academic and professional titles: Use standardized equivalents (e.g., “Consultant Physician,” “Chartered Engineer”) as accepted by licensing bodies.
- Legal references: Represent article numbers, decree titles, and statute names precisely; include transliterations where necessary for cross-reference.
For complex records (e.g., criminal clearance certificates, medical reports, patents), we align with sector terminology by using domain-specific glossaries and reviewer oversight. This ensures your translation not only reads accurately but is also recognized by targeted authorities in Saudi Arabia and abroad.
6) Quality Assurance Translation: How We Minimize Risks
A robust quality framework reduces rejections and rework. At C-KAT Translations and Interpretations, our QA includes:
- Dual-linguist process: Translation by a specialist, review by a second linguist, and final proofreading.
- Consistency control: Termbase and style guide for repeated phrases across multi-document submissions.
- Layout fidelity: Mirrors original structure so courts or ministries can match clauses, seals, and exhibits quickly.
- Confidential handling: Encrypted file exchanges and NDA-backed workflows for sensitive personal and corporate data.
Result: Fewer queries from authorities and a smoother document pathway throughout the certified translation process in Saudi Arabia.
7) Typical Timelines, Costs, and a Fast Certified Translation Process
Time and cost depend on volume, language pairs, and complexity. As a rule of thumb:
- Short personal documents (IDs, certificates): Often within 24–48 hours, faster with priority service.
- Legal and technical files (contracts, medical, engineering): 2–5 business days depending on length and required attestations.
- Legalization and attestation steps: Add days for MOJ/MOFA scheduling, notarization, and embassy appointments.
To accelerate:
- To accelerate the process, please submit clear and complete scans and include any deadlines or appointment dates.
- Pre-verify the requirements with the receiving authority, or request that C-KAT confirm them on your behalf.
- Bundle documents for economies of scale and consistent terminology.
We provide transparent quotes and realistic timelines upfront, with options for expedited processing where feasible in Saudi Arabia.
8) Avoiding Rejections: Common Pitfalls and How to Fix Them
- Unclear purpose: Not telling your provider whether the target is MOJ, MOFA, or a specific embassy can lead to wrong formats. Always specify the destination authority.
- Name inconsistencies: Transliteration that doesn’t match your passport or ID may cause delays. Please provide official identity documents to assist with the correct spelling.
- Missing annexes: Authorities often require all pages, including the backside of cards or seals. Include full scans.
- Outdated legalization sequence: Embassy procedures change. Confirm before you translate.
- Improper formatting: Some entities reject translations without page-by-page seals or proper accuracy statements. Ensure your provider follows official document formatting KSA conventions.
9) Document Types: Personal, Academic, Corporate
We support a broad range of document categories across Saudi Arabia. Each has nuances in document translation procedure KSA:
- Personal status: Birth, marriage, divorce, police clearances, passports, residency permits (Iqama). These often require meticulous transliteration and may need MOFA attestation for use abroad.
- Academic: Diplomas, transcripts, and training certificates. Universities and licensing bodies may require notarization or embassy legalization.
- Corporate and legal: Articles of association, commercial registrations, tax and social insurance records, court judgments, powers of attorney, and contracts. Chamber of Commerce verification may be needed before MOJ/MOFA steps.
- Technical and medical: Manuals, safety data sheets, clinical reports, device registrations. Sector-specific terminology is critical; quality assurance translation reduces regulatory queries.
10) Comparison: Submission Routes and Responsibilities
| Route | Who Requires It | Key Actions | Typical Extras |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOJ (court/legal use) | Courts, legal departments | Certified translation with seals on each page; attach source copies | May require notarized affidavit for certain cases |
| MOFA (use outside KSA) | Individuals and companies sending documents overseas | Certified translation; prior attestations as required | Embassy appointment after MOFA for final legalization |
| Embassy acceptance | Immigration, study, licensing abroad | Embassy-specific requirements: appointment or courier submission | Additional forms and fees; originals often required |
11) Why Choose C-KAT Translations and Interpretations
C-KAT is a Saudi-based certified translation office and language services company officially recognized for legally accepted document translation, attestation, and interpretation services across Saudi Arabia. Our advantages:
- End-to-end compliance: We align with MOJ translation requirements, MOFA, and embassy standards for smooth acceptance.
- Subject-matter expertise: Legal, medical, technical, and academic specialists ensure accuracy.
- Speed with quality: Prioritized workflows and a fast certified translation process when timelines are tight.
- Secure handling: Confidentiality agreements and encrypted file exchange protect your data.
- Beyond translation: Professional interpretation for events, meetings, conferences, and seminars—plus simultaneous interpretation equipment rental and on-site technical support.
Need help planning your document path? Contact C-KAT Translations and Interpretations to confirm requirements and get a clear, obligation-free quote tailored to your Saudi Arabia authority or embassy.
FAQs: Certified Translation in Saudi Arabia

Short personal documents can be delivered within 24–48 hours; complex legal or technical files may take several days. Add buffer time for legalization and attestation steps with MOJ, MOFA, and embassies.
No. Notarization requirements Saudi Arabia depends on the receiving authority. Courts, some ministries, or embassies may request notarized affidavits. Please confirm ahead of time or feel free to ask us to verify.
Some accept secure PDFs, but many still require wet-stamped physical copies. Embassy-accepted translation process rules vary.
We match spellings to official identity documents. If your documents show multiple spellings, we align with the passport and note alternatives if needed for cross-reference.
Yes. We translate commercial registrations, articles, contracts, and financial documents, and guide you on Chamber of Commerce verification, MOJ, MOFA, and embassy steps where applicable.
Conclusion: Navigate the Certified Translation Process Saudi Arabia with Confidence
The certified translation process Saudi Arabia becomes straightforward when you follow a clear, authority-specific checklist—verifying requirements, applying standardized terminology and transliteration, ensuring quality assurance, and completing certification, stamping, and any required legalization. For a broader picture of legal acceptance and document types, revisit our main resource: Read complete overview: “Certified Translation Saudi Arabia: The Complete Guide to Legally Accepted Documents.”
Ready to proceed?
C-KAT Translations and Interpretations offers compliant, confidential, and timely certified translations across Saudi Arabia, plus support with MOJ/MOFA and embassy steps. Share your documents and target authority, and we’ll provide an accurate quote and a reliable path to acceptance.


