When your documents must meet legal and institutional requirements, small details make the difference between approval and rejection. This guide explains the standards and best practices for Arabic-to-English and English-to-Arabic certified translation Riyadh requires for official submissions. You will learn how acceptance works across ministries, courts, universities, embassies, and corporate registries in Riyadh; what “certified” truly means locally; and how to avoid rework caused by formatting, transliteration, or terminology inaccuracies.
For a broader overview of costs, timelines, and service types, see the pillar article:
Read the complete overview: “Certified Translation Riyadh: The Complete Guide to Legally Accepted Documents, Costs, and Processes.”
C-KAT Translations and Interpretations is a Saudi-based certified translation office trusted by individuals, corporations, and government entities for compliant, confidential, and government-approved translation Riyadh-wide. If you need legally accepted documents fast—and without compromise on accuracy—our project teams and on-site technical support can help you plan and execute with confidence.
Table of Contents
What “Certified” Means in Riyadh for Official Documents
In Riyadh, a certified translation is a professional translation that bears a translator’s certification statement, official stamp, signature, and the licensed company’s details to demonstrate responsibility and traceability. For ministries, courts, embassies, and universities, this certification is a key acceptance criterion. Some institutions may also require additional steps such as attestation, legalization, or e-verification. In practice, a government-approved translation Riyadh authorities accept will usually include the following:
- The translator or agency will typically provide a certification statement that affirms the translation’s completeness and accuracy.
- The official stamp and signature must be included, along with company registration details on the certificate or cover page if applicable.
- Document references (source language, target language, document type, page count, date).
- Document integrity markers (page numbers, seals across pages for physical copies, and secure PDFs for digital copies).
- Compliance with any institution-specific submission rules (paper vs. digital; bilingual layout; sealed envelope).
While requirements differ by recipient, the practical standard is to ensure the translation is complete, faithful to the original, formatted to preserve meaning, and signed/stamped by an authorized provider. If you are uncertain which format your recipient expects, C-KAT Translations and Interpretations can confirm requirements in advance and prepare the correct package.
Official Translation Standards Riyadh: Acceptance Essentials
While various authorities enforce distinct submission guidelines, Riyadh widely adheres to the following acceptance standards for certified language translations:
1) Credentials and certifications
- Use a certified translation office that can provide a verifiable certification statement, stamp, and signature.
- Where a specific ministry or university has a preferred list, confirm your provider is acceptable.
- Ensure the certification covers both accuracy and completeness; partial or summary translations are typically rejected.
2) Source Document Integrity
- Provide legible scans or originals with all pages, seals, and endorsements visible.
- Any handwritten annotations, corrections, or marginal notes must be translated or flagged appropriately.
- If originals include multiple languages (e.g., Arabic/English), confirm whether a bilingual translation is still required.
3) Layout and Seal Management
- Preserve original structure: headings, tables, seals, signatures, and footers should be clearly referenced in the translation.
- Affix stamps on all pages where necessary and use tamper-resistant binding for hard copies.
- When submitting electronically, request secure, non-editable PDFs and a separate signed certificate page.
4) Institutional Preferences
- Courts, notaries, and legal registries may require Arabic as the controlling language for filings; plan for dual-language formatting to Riyadh standards if bilingual presentation is requested.
- Universities and professional licensing bodies often require consistent name transliteration and full grades/credit details.
- Corporate registries and chambers may require seals and signatory details on the certification page.
Pro tip: When in doubt, share the target institution’s request letter or link to their guidelines. C-KAT can align your English-to-Arabic certified translation Riyadh institutions expect with the exact format and seals.
Terminology Accuracy Riyadh: Why Precision Matters
Terminology accuracy Riyadh standards demand is not only about choosing the right words—it is about preserving legal effect, technical meaning, and contextual nuance. Misinterpretation in legal, financial, medical, or academic documents can cause delays, refusals, or compliance issues. Consider the following principles:
- Use established legal and administrative terms accepted in Saudi practice (e.g., powers of attorney, articles of association, court orders, and MOFA attestations).
- Maintain consistent term bases across document sets (e.g., company names, roles/titles, technical nomenclature, and departmental names).
- Respect date systems: when necessary, render both Gregorian and Hijri, and specify the calendar used.
- Avoid adding or omitting content; if the original text is illegible or ambiguous, insert an editorial note (e.g., “illegible stamp” or “[unclear]”) to prevent assumptions.
At C-KAT Translations and Interpretations, terminology management includes vetted glossaries, second-linguist review, and a final compliance assessment before stamping. This disciplined workflow supports a government-approved translation Riyadh offices are more likely to accept on the first submission.
International Organization for Standardization. (2015). ISO 17100:2015 translation services—Requirements for translation services. ISO. https://www.iso.org/standard/59149.html
Ministry of Justice of Saudi Arabia. (n.d.). Translation and legal documentation regulations. Government of Saudi Arabia. https://www.moj.gov.sa
Transliteration Rules Riyadh: Names, Places, and Legal Consistency
Transliteration is often where applications fail. If the spelling of a person’s or company’s name varies between documents, some authorities will reject the file or request notarized reconciliations. To align with transliteration rules Riyadh institutions commonly expect, adopt these practices:
- Match the passport or national ID transliteration for personal names, even if another spelling seems more natural.
- For company names, match the commercial registration (CR) spelling. If rebranding or alternate spellings exist, include a statement of equivalence when acceptable.
- Keep diacritics simple for English target texts; avoid inconsistent hyphenation (e.g., Al Rahman vs. Al-Rahman vs. Alrahman).
- Standardize frequently variable consonants and vowels (e.g., Muhammad vs. Mohammed vs. Mohammad) across the entire document set.
Example: Common Arabic-to-English Transliteration Choices
| Arabic | Typical English Variants | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| محمد | Muhammad, Mohammed, Mohammad | Follow passport/ID; keep consistent across documents |
| عبدالله | Abdullah, Abdulla | Use official ID spelling; avoid mixing |
| الرياض | Riyadh, Ar Riyadh | Use the standardized form “Riyadh” unless an official record uses another. |
When reconciling name variants, include a brief note in the certification or a translator’s footnote if acceptable to the receiving authority. C-KAT’s team will advise when a separate affidavit or notarial statement is recommended.
Dual-Language Formatting Riyadh: Side-by-Side vs. Top-and-Bottom
Dual-language formatting Riyadh recipients may request depends on how the translated document will be used. Courts and registries may prefer Arabic-first or Arabic-only for controlling effect, whereas universities and employers might accept bilingual layouts. Two common options:
| Format | Use Cases | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Side-by-Side (Arabic | English) | Contracts, certificates, transcripts, technical specs | Immediate comparison; preserves tables and seals context | Requires skilled RTL/LTR formatting; may increase page count |
| Top-and-Bottom (Arabic above, English below) | Court filings, notarial records, tender documents. | There is a clear separation between the two languages, which often makes stamping and binding simpler. | Cross-referencing elements (e.g., tables) requires careful pagination. |
In all cases, ensure seals and signatures are referenced in the target language (e.g., “Seal: Ministry of…”), and maintain page numbering consistency. C-KAT’s production team handles complex multilingual layouts, ensuring your English-to-Arabic translation Riyadh authorities receive is both readable and compliant.
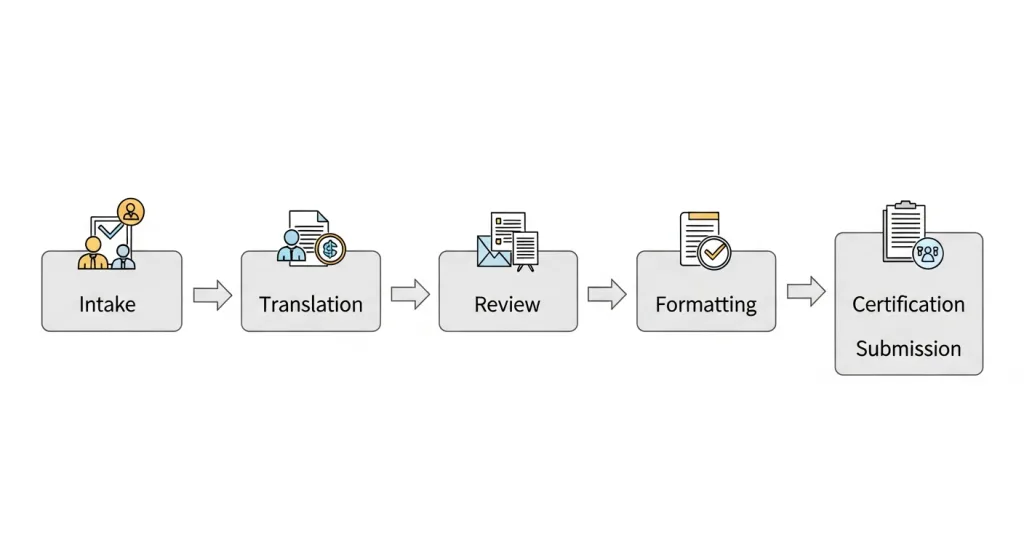
Step-by-Step: How to Secure an English-to-Arabic Certified Translation Riyadh Institutions Accept
- Collect your source documents. Include all pages, stamps, endorsements, and attachments. For any poor-quality scans, please provide clearer copies or the originals.
- Confirm destination requirements. Share any request letters or links from the recipient (court, ministry, university, embassy) with C-KAT.
- Request a scoped quotation. We assess complexity, volume, formatting needs, and deadlines. If attestation or legalization is required, we plan those steps too.
- Translation and review. Dedicated linguists translate, and a second linguist reviews. Terminology and transliteration are checked against your IDs and corporate records.
- Formatting and QA. We align the layout to official translation standards Riyadh bodies specify, including bilingual options and page-by-page seal references.
- Certification and stamping. We issue a certification statement, apply the official stamp and signature, and prepare secure PDFs or bound physical copies as requested.
- Submission support. If needed, we coordinate attestation steps or provide guidance on in-person vs. e-submission preferences. We can also supply additional sets quickly.
Whether you are translating a power of attorney, court judgment, academic transcript, or corporate bylaws, this process ensures a complete and compliant package for Riyadh recipients.
Common Use Cases and How Standards Apply
Legal and Court Documents
- Examples: Court orders, judgments, POAs, contracts, and notarial deeds.
- Key points to remember include: Arabic often taking precedence in court filings, an Arabic-first layout being prioritized, seals and exhibits being cited, and dates being presented in the required calendar format.
Academic and Professional Documents
- Examples: Diplomas, transcripts, training certificates, and professional licenses.
- Key points: Precisely translate grades/credits; maintain standard nomenclature (e.g., GPA scales); ensure name spelling matches passport/ID.
Civil Status and Immigration
- Examples: birth, marriage, or divorce certificates, immigration records, and police clearances.
- Key points: Translate every stamp and endorsement; include both Gregorian and Hijri dates when present; maintain consistent transliteration across the entire application.
Corporate and Commercial
- Examples: Articles of association, CR extracts, board resolutions, tenders.
- Key points: Use established Saudi commercial terminology; ensure company names/titles match CR records; select a dual-language format suitable for filings.
For each scenario, C-KAT ensures the certified language translation Riyadh stakeholders expect is delivered in the most acceptable format.
Formatting and Submission Tips Specific to Riyadh
- RTL/LTR integrity: Maintain proper right-to-left flow for Arabic paragraphs and tables; avoid mixed-direction line breaks that confuse reviewers.
- Seals and stamps: Clearly reproduce or describe seals; if a seal is illegible, note it neutrally (e.g., “illegible circular seal”).
- Units and measures: Convert units only if the original text specifies; otherwise, translate labels and leave figures unchanged with a note if necessary.
- Digital vs. hard copy: Some recipients accept secure PDFs; others prefer sealed and bound hard copies. Verify early to prevent reprinting.
- Attachments and exhibits: Translate exhibit labels, maintain numbering, and ensure cross-referencing matches in both languages.
These practical considerations are core to the official translation standards Riyadh reviewers apply during evaluation.
Quality Assurance and Confidentiality at C-KAT
To protect your data and ensure top-tier quality, C-KAT Translations and Interpretations uses structured workflows aligned with industry best practices:
- Two-step linguistic review: Translator + independent reviewer model for error reduction and terminology consistency.
- Named-responsibility certification: Clear chain-of-custody on who translated, reviewed, and certified your file.
- Secure handling: Encrypted file exchange and secure PDFs for digital delivery; sealed and bound sets for physical submissions.
- Bilingual QA: Dual check on high-stakes items (names, dates, figures, serial numbers, legal provisions).
For events, meetings, and conferences in Riyadh, C-KAT also provides professional interpretation, simultaneous interpretation equipment, and on-site technical support—ensuring your multilingual communication is consistent across spoken and written channels.
Coordination with Attestation and Legalization
Some documents need more than certification. They may require institutional attestations (e.g., Chamber of Commerce), embassy legalization, or acknowledgments by notarial services. Steps vary by destination and purpose. C-KAT coordinates with you on:
- Whether certified translation alone suffices for the recipient.
- Attestation sequences after translation (e.g., from a local authority before submission).
- Expected lead times and whether e-portals accept digital copies or require in-person submissions.
Ministry of Justice of Saudi Arabia. (n.d.). E-services and procedural guidelines for document submission. Government of Saudi Arabia. https://www.moj.gov.sa/wps/portal/Home/EServices
FAQ: English-to-Arabic Certified Translation Riyadh
Many accept secure, non-editable PDFs with a certification page, but some still require sealed and bound hard copies. Please verify the preferred submission format before finalizing. C-KAT can provide both.
Translate what appears in the source and, where advantageous or required, include both calendars with clear labels (e.g., AH vs. AD). Consistency is essential across the file set.
Yes. Align transliteration with official IDs or CR records. Inconsistent spellings are a leading cause of rejections. If variants exist, consult C-KAT for reconciliation strategies.
No. Certification is the translator/agency’s attestation of accuracy. Notarization or legalization are separate steps some recipients require. Determine these early to avoid delays.
Yes. Stamps and seals should be translated or described. If any are unclear, the translation should indicate this neutrally. Clear reproduction supports acceptance.
Conclusion: Get English-to-Arabic Certified Translation Riyadh Demands—Right the First Time
For legally accepted submissions, precision in terminology, transliteration, and layout is non-negotiable. By following the standards in this guide and partnering with a trusted provider, you can secure English-to-Arabic certified translations Riyadh institutions accept without unnecessary rework. C-KAT Translations and Interpretations delivers compliant, confidential, and timely translations—plus attestation coordination and bilingual formatting expertise—so your documents move forward smoothly. Ready to proceed?
Contact C-KAT for a quick assessment and quote.
For a broader view of processes and pricing, see the pillar article: Read the complete overview: “Certified Translation Riyadh: The Complete Guide to Legally Accepted Documents, Costs, and Processes.”




