Certified translation plays a decisive role in how governments, courts, universities, and embassies evaluate your documents. Whether you are submitting a visa application, filing a court case, registering a business, proving academic credentials, or coordinating multi-country corporate transactions, the accuracy and legal acceptance of your translations directly affects outcomes.
This complete guide explains what certified translation is, how it works, who accepts it, how to avoid rejections, and what it costs. It is written for individuals, legal and immigration professionals, corporate teams, academic administrators, and government partners seeking clarity, reliability, and compliance. Throughout, we outline practical steps to streamline your process and reduce risk. If you are seeking certified translation Riyadh solutions that meet legal and institutional standards, use this guide as your authoritative starting point.
Table of Contents
Quick Summary
A certified translation is a formally verified translation with a declaration of accuracy, translator or agency identification, date, and often a stamp or seal. It is typically required for civil status records, court exhibits, immigration files, academic records, business registrations, and medical papers. Acceptance depends on the receiving authority, and some cases require additional notarization or legalization.
Costs vary by language pair, specialization, word count, formatting, and urgency. Turnaround can range from the same day for simple items to several business days for complex or multi-language files. Use a reputable provider with qualified translators, robust quality assurance, confidentiality controls, and documented compliance procedures to ensure smooth acceptance.
What Is Certified Translation, and When Do You Need It?
A certified translation is a full and accurate version of a document that comes with a signed statement confirming that the translation is correct and complete. The certification statement is issued by a qualified translator or a recognized translation company, and it typically includes a signature, date, and official stamp. Many authorities require attachments such as translator credentials or agency letterhead. Certified translations are often requested for civil registry documents, court filings, contracts, visa and immigration dossiers, educational admissions, professional licensing, and company formation packages.
Unlike general translation for internal use, certified translation Riyadh is designed to be reviewable and auditable. It preserves the structure, data, seals, and stamps of the original to the greatest extent possible. Some scenarios also require notarization or legalization. The key is to match the echelon of formality to the receiving institution’s exact rules.
for detailed information: read “Legalized vs Certified vs Notarized Translation Riyadh: What You Need and When“
Documents Commonly Requiring Certification
While any document can undergo certification upon request, law or policy frequently mandates several categories. Your use case and the destination authority determine which set of requirements applies. Below is a non-exhaustive overview.
Civil and Personal Records
- Birth, marriage, and divorce certificates
- National IDs, passports, residency permits
- Police clearance certificates
Legal and Court Materials
- Contracts, powers of attorney, affidavits, legal opinions
- Court judgments, pleadings, evidence exhibits
- Company bylaws, articles of association
Academic and Professional
- Diplomas, transcripts, letters of enrollment and graduation
- Professional licenses, continuing education certificates
- Academic research records and attestations
Corporate and Financial
- Commercial registrations, tax and VAT documents
- Invoices, purchase orders, tenders, proposals
- HR files and employment contracts
Medical and Health
- Discharge summaries, lab reports, imaging results
- Vaccination cards, medical histories
- Clinical trial and research documentation
Tip: Ask the receiving institution whether they have language, format, or certification preferences. Some request the original language and translation side by side, while others stipulate separate packets.
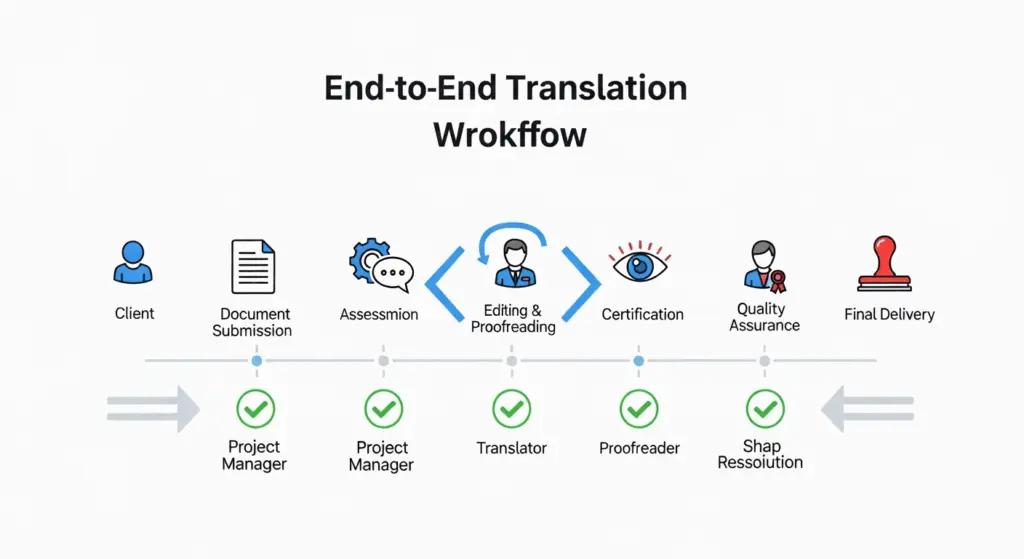
How the Certified Translation Riyadh Process Works
The pathway from document intake to delivery follows a predictable series of steps that safeguard accuracy, traceability, and compliance. Understanding this workflow helps you prepare your files and timelines.
- Scope confirmation and intake: You receive a quote based on document type, language pair, complexity, formatting, and urgency. Clarify acceptance requirements such as certification wording, stamp style, notarization, or legalization.
- Source review and file preparation: The team checks legibility, page count, and presence of seals and stamps and specifies any missing pages or issues to resolve before translation begins.
- Translation by a qualified linguist: A domain-appropriate translator renders the text faithfully, marking seals, signatures, and handwritten notes as needed. Sensitive numbers and names are double-checked.
- Editing and quality review: A second linguist or reviewer verifies terminology, consistency, formatting, and compliance with any provided style or reference materials.
- Certification and stamping: A signed statement and official stamp or seal are appended, including identification of the translator or agency, date, and relevant references. If requested, notarization is arranged as a separate step.
- Delivery and archiving: Certified copies are delivered in physical or secured digital formats based on the recipient’s policy. Files are archived in a controlled manner for future reference.
Quality Standards, Linguistic Accuracy, and Data Security
Certified translations must be accurate, complete, and traceable. To achieve that, providers build their services on standardized processes and clearly defined quality goals.
Linguistic Quality and Formatting
- Terminology management: Glossaries and termbases ensure consistent usage of legal, academic, medical, or corporate vocabulary.
- Formatting fidelity: Layout mirrors critical elements such as tables, seals, and stamps. The translation should not obscure original data.
- Reviewer independence: A second set of eyes is essential for catching inconsistencies and ensuring compliance.
Accuracy of Names, Numbers, and Seals
- Proper transcription of names using standardized romanization or official spellings.
- Careful reproduction of dates, file numbers, registry entries, and monetary amounts.
- The system clearly indicates official seals, watermarks, and signatures.
Confidentiality and Security
- Secure file transfer and storage using encrypted channels.
- Access controls and confidentiality agreements for staff and linguists.
- Document traceability and audit logs for regulated contexts.
Who Accepts Certified Translations and What They Expect?
Courts, ministries, regulators, embassies and consulates, universities, licensing bodies, and corporate compliance teams commonly accept certified translations. While general principles are similar across institutions, each authority may specify its own rules for language pairs, certification text, stamps, paper or digital delivery, number of copies, and whether notarization or legalization is required. Always request written guidance from the receiving authority to avoid delay.
Courts and Legal Proceedings
Courts typically require precise formatting and explicit mention that the translation is a true and complete rendering. Some jurisdictions request translations by recognized or court-registered translators. Evidentiary materials can demand line-by-line fidelity and transparent annotation of stamps and seals. Ask for the court’s practice directions regarding translation for courts.
Universities and Professional Bodies
Academic admissions, credential evaluations, and licensing applications seek accurate representation of grades, credit hours, and institutional seals. They sometimes require sealed envelopes or signed cover sheets. Please confirm their policy on translation for universities and whether electronic copies are acceptable.
Embassies and Consulates
Consular sections can be strict about certification wording, sequencing of notarization or legalization, and the submission of originals alongside translations. Appointment systems and digital portals may impose specific file size or format constraints.
Regulatory Compliance and Recognition
Authorities generally expect translators and agencies to be demonstrably qualified. Some procedures require translators approved or recognized by relevant ministries. Others require adherence to defined quality frameworks and documentation of the certification process. When in doubt, obtain written acceptance criteria from the recipient and confirm whether your chosen provider meets them.
Industry Applications and Examples
Certified translations intersect with multiple industries, each with its own patterns of documents, risk profiles, and compliance expectations.
Legal
Law firms handle contracts, court submissions, evidential exhibits, and legal opinions. The emphasis is on precision, traceability, and adherence to procedural rules. Working with legally specialized translators reduces risk and revision cycles.
Immigration
Immigration filings involve identity documents, civil status records, education credentials, and work histories. Consistency of names and dates is essential to prevent mismatch flags in cross-checking systems.
Education and Academic
Admissions and credential evaluations require transcripts, diplomas, syllabi, and institutional attestations. A strong focus on formatting and seal replication helps ensure smooth evaluation.
Business and Corporate
Company formation, regulatory filings, compliance audits, tenders, and vendor onboarding often require certified translations. Clear version control and document traceability are critical in audits.
Medical
Patients and providers rely on certified translations for discharge summaries, lab results, and care plans. Accuracy affects health outcomes and insurance coverage decisions.
Turnaround Times and Managing Urgent Requests
Turnaround depends on document length, complexity, domain specialization, language pair, required formatting, and whether notarization or legalization steps are included. Simple civil documents can often be completed within 1 to 2 business days. Complex legal or academic records with tables and seals may require 3 to 5 business days or more. Time-sensitive requests are possible in many scenarios, but they should be balanced against quality and acceptance risk. Communicate challenging deadlines early, and ask about staggered delivery for multi-document packages.
- Express options: Same day or next day for short, legible documents.
- Parallel processing: Larger projects can be split among qualified translators with a unified glossary to maintain consistency.
- Post-translation steps: Allow time for notarization or legalization if required by your recipient.
Pricing, Cost Factors, and a Practical Comparison
Certified translation Riyadh pricing reflects the scope and risk of the assignment. Common cost drivers include document length or page count, language pair, subject matter specialization, formatting complexity, certification or notarization needs, and urgency. A transparent quote should itemize these elements and indicate any optional add-ons, such as notarization or legalization.
Key Cost Drivers
- Language pair: Rare combinations tend to be more expensive.
- Complexity: Legal, medical, or academic texts often require domain specialists.
- Formatting: Reproducing tables, stamps, and non-editable scans adds time.
- Volume: Bulk discounts may apply for multiple documents from the same client.
- Urgency: Express surcharges reflect overtime and parallel resourcing.
Comparison Table
| Type | What It Is | Common Uses | Who Typically Requires It | Relative Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certified Translation in Riyadh | Translation with a signed statement attesting accuracy and completeness, often with stamp | Civil records, court exhibits, immigration files, academic records, corporate documents | Courts, embassies, universities, ministries, regulators | Base | Most widely required format for official use |
| Notarized Translation | Certification statement is notarized by a notary public | When an authority requests notarization in addition to certification | Some consulates, agencies, or registrars | Base + Notary Fee | Separate from translation quality; confirms identity of signer |
| Legalization or Attestation | Authentication of signatures or documents by designated authorities | Cross-border submissions that need formal validation | Foreign ministries, embassies, specific agencies | Additional Fees | Sequence and authorities vary by destination |
Notarization, Legalization, and When They Are Needed
Certification, notarization, and legalization each serve different purposes. Certification attests to translation accuracy. Notarization attests to the identity of the person signing the certification statement. Legalization or attestation confirms the authenticity of signatures or documents through designated authorities. Some cases require only certification. Others require certification plus notarization. Cross-border filings can require multi-step legalization with specified authorities. Verify the exact sequence with the receiving body to prevent rework.
Checklist:
- Confirm whether certification alone is sufficient.
- Ask if a notary is required and whether they must be in a specific jurisdiction.
- For international use, please confirm the legalization steps and whether originals are required.
Beyond Translation: Interpretation and Event Support
Many organizations require not only document translation but also live language support for meetings, hearings, conferences, and seminars. Professional interpretation services include simultaneous, consecutive, and liaison modes. For larger events, simultaneous interpretation equipment and technical support are critical for audio quality and audience experience. Coordinating interpreters, booths, headsets, and a sound engineer ensures smooth delivery and compliance with event protocols.
Decision-Making Framework: How to Select the Right Provider
Use the following framework to choose a certified translation Riyadh partner aligned with your goals, timelines, and compliance obligations.
- Define the acceptance criteria: Identify the receiving authority and their rules. Obtain written guidance whenever possible.
- Match expertise to your domain: Legal, immigration, academic, medical, and corporate documents benefit from domain-savvy linguists.
- Review translator qualifications: Confirm relevant credentials, approvals, or recognition where applicable.
- Verify quality assurance: Ask about editing, proofreading, and final sign-off. Request sample certification statements.
- Assess confidentiality controls: Ensure secure transfer, storage, and restricted access for sensitive data.
- Review turnaround and capacity: Confirm realistic delivery schedules and options for urgent cases.
- Clarify formatting and stamp replication: Confirm approaches to seals, tables, and complex layouts.
- Understand pricing and add-ons: Ensure transparent quotes covering certification, notarization, and any legalization steps.
- Ask about references and acceptance history: Look for a track record with courts, universities, and embassies.
- Plan for future needs: Choose a partner who can scale across languages and services, including interpretation for live events.
Riyadh Location-Based Guide: Local Acceptance, Offices, and Practical Tips
This section focuses specifically on Riyadh and the local environment for certified translations. If you are searching for a certified translation office in Riyadh, official document translation in Riyadh, or translation services near me in Riyadh, consider the acceptance rules of courts, ministries, universities, and embassies, plus the logistics of notarization and document legalization in Riyadh.
Local Acceptance and Government Bodies
- Government-approved translation Riyadh: Confirm whether your recipient requires translators recognized by relevant ministries or departments. Some processes require MOJ-approved translators in Riyadh for legal matters.
- Translation for courts Riyadh: Courts often request full fidelity to the source, proper certification wording, and clear reproduction of seals and stamps. Request their specific practice notes.
- Translation for universities Riyadh: Admissions and registrations can have specific rules on sealed envelopes or digital submission formats. Confirm if they accept scanned certified copies or require physical originals.
Embassies and Consulates in Riyadh
- The embassy accepted the translation Riyadh: Many consular sections publish guidance on certification, notarization, and legalization sequences. Bookmark their websites and appointment systems.
- Visa document translation Riyadh: Visa centers may require translations for civil status records, bank statements, and employment letters. Double-check acceptable languages and file formats.
Document Types and Language Pairs
- Birth certificate translation in Riyadh and academic certificate translation Riyadh are among the most requested services. Ensure that names and dates match all other documents in your file.
- Arabic to English translation Riyadh and English-to-Arabic translation Riyadh are the most common pairs. Please confirm the availability and lead times for other language combinations.
Notarization and Legalization Logistics
- Notarized translation Riyadh: Some cases require a notary to verify the identity of the signer of the certification statement.
- Document legalization Riyadh: Depending on the destination, you may need multi-step attestation by designated authorities. Please confirm the sequence and appointment requirements in advance.
Turnaround and Service Model
- Fast translation Riyadh and urgent certified translation Riyadh services are common, but availability depends on document complexity, volume, and whether notarization or legalization is needed.
- Immigration translation Riyadh often involves multiple documents; plan for batch submission and consistent formatting across the set.
If proximity is a priority, search for “translation services near me in Riyadh” If acceptance and specialization matter more, choose the provider with the strongest track record for your document type and receiving authority. Contact C-KAT Translations and Interpretations for expert assistance.
Decision Checklist and Risk Controls
Use this shorthand checklist before you submit any certified translation for official use.
- Recipient confirmed: name of authority, country, and any published translation rules.
- Language pair confirmed: Verify the required target language and variant.
- Certification statement: Review wording, signature, date, and stamp template.
- Names and dates: Align spellings and formats across your entire dossier.
- Notarization or legalization: Identify steps, fees, and appointment lead times.
- Delivery format: Printed originals, scanned copies, or secure digital submission.
- Backup buffer: Allow time for edits if the recipient requests adjustments.
Ministry of Foreign Affairs – Saudi Arabia. (n.d.). Ratification services on documents. Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved December 10, 2025, from https://www.mofa.gov.sa/en/eservices/Pages/svc31.aspx
Royal Consulate General of Saudi Arabia, Karachi. (n.d.). Rules & regulations for attestation process [PDF]. Ministry of Foreign Affairs – Saudi Arabia. Retrieved December 10, 2025, from https://embassies.mofa.gov.sa/sites/pakistan/EN/karachi/AboutDiplomaticMission/SiteAssets/Pages/Consulate-Services/%E2%80%A2Instructions%20for%20%20Attestation.pdf
FAQ: Certified Translation Riyadh Key Questions Answered
A certified translation includes a signed declaration by the translator or agency attesting that the translation is a true and complete rendering of the original. It often carries a stamp, date, and contact identification.
Not necessarily. Notarization is only required if the receiving authority requests it. It confirms the identity of the person who signed the certification statement, not the quality of the translation itself.
Acceptance is jurisdiction specific. Always check written instructions from the receiving institution and share them with your provider to ensure compliance. Some authorities specify exact wording, seals, or additional steps like legalization.
Simple civil documents can often be completed within 1 to 2 business days. Complex files, rare language pairs, and additional steps like notarization or legalization add time. Communicate your deadline early.
Typically the translator or agency name, a declaration of accuracy, date, signature, and an official stamp. Some recipients request translator credentials or ID numbers on the statement.
Stamps and seals are reproduced descriptively in the translation. If legible text appears inside a seal, that text is translated with an indication that it is part of a seal.
Poor scans risk rejection. Provide clear, complete scans of all pages and both sides where relevant. Ask your provider to flag any issues before translation begins.
Many providers can issue both. Confirm the recipient’s policy. Some require original stamped paper, while others accept secure digital files.
Provide the official spelling used on your primary identity document and explain variations. Consistent spelling across the translation set reduces mismatch flags.
Obtain the recipient’s rules, prepare clean scans, confirm certification wording, and work with a provider experienced with your document type and authority. If in doubt, request a pre-submission review.
Conclusion
Certified translation is a compliance-driven service that directly impacts legal outcomes, academic admissions, immigration approvals, and corporate operations. This guide clarified what certified translation means, who requires it, how the process works, key quality and security controls, and practical steps to manage timelines and cost.
If you need certified translation Riyadh solutions that satisfy courts, ministries, universities, and embassies, partner with a provider that demonstrates deep process discipline and regulatory awareness.
C-KAT Translations and Interpretations is a Saudi-based certified translation office and language services company recognized for legally accepted document translation, attestation, and interpretation services across Saudi Arabia. We serve individuals, corporates, and government entities with accurate, confidential, and compliant translations, along with professional interpretation and on-site technical support. Contact C-KAT Translations and Interpretations for expert assistance.


